facio ut des
principle of the roman civil law
The Micro-Biology Consult Dr. Andreas Hassl intention
Table of contents:
- M2.1Hygiene and Vivaristic
- M2.2Infectious Disease Ecology & Microbiological Conservation Medicine
- M2.3Parasite detection in waters and environmental samples
- M2.4Opportunists in amphibians and reptiles
- M2.5Faunistic studies
- M2.6Archeomicrobiology
- M2.7Law and (Micro-)Biology
- M2.8Manufaction and trade
In this chapter the current activities of the office Micro-Biology Consult Dr. Andreas Hassl are to be presented. This compilation describes and delimits the fields of professional competence. The purpose is to assist contractors of expert opinions during the preparation for a selection of an expert - and thus to prevent both sides with embarrassing allegations because of the lack of necessary abilities before the contract conclusion. All persons able to make a substantial contribution to these fields of competence or to bring in their thoughts and ideas are invited with pleasure to contact me (by e-mail or telephone).
M2.1 Hygiene and Vivaristic
Fig. 1: A frog with Weeksella-colonized finger cysts © A. Hassl.
In the cities of the industrial nations more and more exotic pet animals, in particular reptiles, are held. These wild animals kept in captivity, their fodder organisms, usually rodents and insects, and the human nurses and contact people form a new reservoir for those microorganisms, which are able to infect any of these host taxa. Representatives of this group of microorganisms are found in the free-living, opportunistic amoebas, the staphylococci, Weeksella and Salmonella, and also in the genus Cryptosporidia. A reduction of this microbial flora dangerous for man and animals by practicable hygienic processes was a central request of the office Micro-Biology Consult Dr. Andreas Hassl. The office sees itself as an advisory partner and service company for owners of exotic pets. The following issues were dealt with in detail:
- I.1 Cryptosporida and cryptosporidiosis in amphibians and reptilians.
- I.2 Pattern of Salmonella Excretion in Amphibians and Reptiles in a Vivarium.
- I.3 Sentinel microorganisms for a microbiological evaluation of vivaria.
- I.4 Salmonella and Yersinia-infections in captive amphibians and reptiles.
- I.5 Hygienic evaluation of terraria inhabited by amphibians and reptiles: cryptosporidia, free-living amoebas, salmonella.
M2.2 Infectious Disease Ecology & Microbiological Conservation Medicine
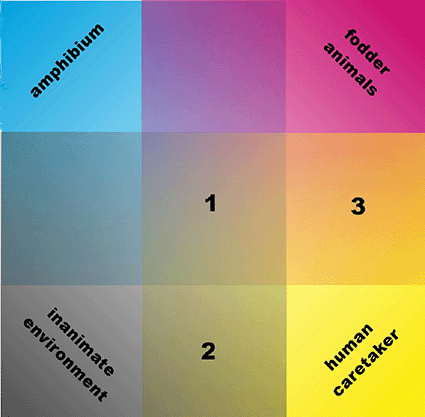
Fig. 2: The intersection. © A. Hassl.
My special interests are focusing on a registration and a risk assessment of diseases caused by mostly opportunistic behaving infectious microorganisms associated with the keeping of amphibians and reptilians. My special interest lies with the microbiology and the hygienic problems of the intersection man - exotic pet animal - feeder organisms - terrarium. The microbiological fauna of this intersection is characterised by the appearance of a special type of infectious microorganisms, in most cases these microorganisms can infect a wide variety of hosts and they cause opportunistic infections. These ill-defined groups of microorganisms only colonize or transitionally infect an immunocompetent host. But it may cause even lethal disease in an immunologically debilitated animal or man, in rare cases even in amphibians, reptilians, fodder animals and man mutually. The following issues were dealt with in detail:
- II.1 Preventive microbiological investigations in captive reptiles and amphibians.
- II.2 Microbiological Conservation Medicine and Exotic Pets.
- II.3 Well-intentioned misfeature - mismanagement of exotic pets.
- II.4 Diseases and Defence Mechanisms in frogs, toads, salamanders and newts.
- II.5 Pet Amphibian Keeping in Central Europe: Underestimated Contagious Hobby.
- II.6 Captive Snake' Care as Parasite's Life Cycle Conservation Program.
- II.7 Exotic pets as source of a biological hazard for transmission of parasites to man.
M2.3 Parasite detection in waters and environmental samples
Fig. 3: Cryptosporidia-findings in Lower Austria. © A. Hassl.
Lamblia- and Entamoeba-cysts as well as Cryptosporida- and Toxplasma gondii-oocysts are stages of life of microorganisms pathogenic for man and domestic animals, which may be transmitted to new hosts by drinking water, water for human consumption, and mud. Usually waterborne diseases are considered as problems of undeveloped countries with inadequate sanitary practices. There is, however, an increasing recognition of the Central European, industrialized countries public health problems caused by use of only partially or insufficiently treated domestic waters, emanating from the public water supplies. Especially waterborne microbial diseases, one and a half century ago expected to be eliminated as public health problems, not only remains the leading cause of death worldwide, but the spectrum of disease is expanding and the incidence of many waterborne microbial diseases is increasing. The detection of such microorganisms, their species differentiation, and the finding of their virulence and aliveness, usually by means of gene technology, are developments, which were run in particular in the late Clinical Institute of Hygiene and Medical Microbiology of the Medical University Vienna as a public service mandate. The following issues were dealt with in detail:
- III.1 Detection of Cryptosporidium sp. oocysts in faecal and water samples in Austria.
M2.4 Opportunistic microorganisms in amphibians and reptiles
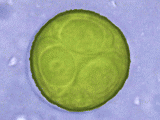
Fig. 4: An Oocyst of an Apicomplexa. © A. Hassl.
The longer life expectancy of captive amphibians and reptiles as well as the increased stress of free-living specimen of these groups of animals by environmental impacts lead to the occurrence of immunosuppression in these animals. This phenomenon and the modifications in the intermediate host fauna clear the way for the establishment of opportunistic microorganisms, eg amoebas, mycobacteria, blood parasites and of exotic, imported parasites. The main emphasis of my studies is focused on the colonisation of amphibians with opportunistic microorganisms. The following issues were dealt with in detail:
- IV.1 A mycobacterial infection in a reptilian pet and the pet keeper - a cause of a zoonosis?
- IV.2 Free-living, opportunistic amoeba as parasites of captive amphibians and reptiles.
- IV.3 Weeksella virosa colonised epidermal cysts in a green frog Hyla crepitans.
M2.5 Faunistic studies
Fig. 5: Herpetophagic ticks in Austria. © A. Hassl.
The determination of the biological species of the pathogen of a parasitosis or a parasite-infection and of the causative agent of a hygienic problem and the consultation of the client over fight and avoidance are the most important pillars of the activity of the office Micro-Biology Consult Dr. Andreas Hassl. As the microbial fauna of man and (pet-)animals in Eastern Austria is known only fragmentarily still, epidemiological questions are important contributions to the hygiene. In particular, the determination of molesting insects and other arthropods and the risk assessment of infestations with arthropods are fundamental working areas of the office Micro-Biology Consult Dr. Andreas Hassl. The following issues were dealt with in detail:
- V.1 Reptile Ticks in Central Europe and the Mediterranean area.
- V.2 An ectoparasite of lizards and a possible vector: the mammal hard tick Haemaphysalis concinna.
- V.3 Age-dependent alterations in a 24-years old Ocellated Lizard.
- V.4 A case of a facultative life-cycle diversification in the fluke Pleurogenoides sp.
- V.5 Identifying parasites as substitution causes in populations of local and allochthone turtles in Lower Austria.
- V.6 Catching European Hamsters in the late medieval Lower Austria.
- V.7 Isolation and purification of antibodies from snake eggs.
M2.6 Archeomicrobiology
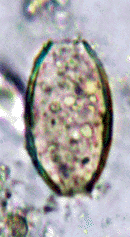
Fig. 6: An egg of a helminth in the borrow of a pit latrine. © A. Hassl.
The making of snap-shots of historic-infectious diseases and the evaluation of their significance for the process of historical events are particularly challenging research directions. It unites humanistic and scientific questions and attempts of explanation. Infections are one of the most important factors in the development of mankind and the evolution of the defence against disease-causing agents, more exactly the evolution of immunological self-recognition, is driving force behind the emergence of new species, man and his specific parasites (s.l.) also. Therefore questions from the field archeomicrobiology are a scientific passion of the cooperating workers of the office Micro-Biology Consult Dr. Andreas Hassl. The following issues were dealt with in detail:
- VI.1 The significance of malaria in the Western Roman Empire.
- VI.2 Biological analysis of late-medieval and modern shards and other specimens from Vienna and Upper Austria.
- VI.3 Hygiene and welfare for invalids in the late-medieval St. Pölten.
- VI.4 The parasite of the Greek antiquity.
- VI.5 The determination of helminth eggs from borrows of medieval and early modern pit latrines.
M2.7 Law and (Micro-)Biology
Fig. 7: The Logo of the legal cursus. © A. Hassl.
Rights serve the performance of the society and they affect the values and they are affected by the units of value of the community. Therefore the conceptions of the society, how problems in species-, animal- and environmental protection can be solved, depend on the law inventory. This inventory is adapted sequentially to changing units of value - the combination of rights and biology obviates economically expensive and socio-politically undesirable erroneous trends. Laws must meet scientific facts, if they do not, they are wastes of economic resources. During the formulation of a law the legislation depends on the realizations of science. The creation of a relation between the two ranges is a special feature of the office Micro-Biology Consult Dr. Andreas Hassl. The following issues were dealt with in detail:
- VII.1 Annotation to the requirements of reptile sales presentation.
- VII.2 Exotic Pet keeping under current Austrian laws.
- VII.3 An ironical comment on the New Austrian Animal Protection Legislation.
- VII.4 Bioethics in parasitology and exotic pet keeping.
- VII.5 Law and the exposure of turtles in Vienna and Lower Austria.
- VII.6 Protection of Endangered Species: The interplay between aesthetics, law, economics and evolution.
M2.8 Manufacturing and trade
Fig. 8: A poster out-of-own-production. © A. Hassl.
The office Micro-Biology Consult Dr. Andreas Hassl produces some microbiological specialities: microscopic slides, antigens for allergy testing, a remedy for the intestinal flora, posters, and reprints. Moreover, food, animal feeding stuff and hunting products are manufactured and sold.
 Andreas R. Hassl
Andreas R. Hassl